Suma de la serie (n+1)/(n+3)*(x+2)^n
Solución
Ha introducido
[src]
oo ___ \ ` \ n + 1 n ) -----*(x + 2) / n + 3 /__, n = 0
Sum(((n + 1)/(n + 3))*(x + 2)^n, (n, 0, oo))
Radio de convergencia de la serie de potencias
Se da una serie:
Es la serie del tipo
- serie de potencias.
El radio de convergencia de la serie de potencias puede calcularse por la fórmula:
En nuestro caso
y
,
,
entonces
Tomamos como el límite
hallamos
Es la serie del tipo
- serie de potencias.
El radio de convergencia de la serie de potencias puede calcularse por la fórmula:
En nuestro caso
y
,
,
entonces
Tomamos como el límite
hallamos
Respuesta
[src]
// 3*x \
// / 2 \ \ || -6 - --- |
||/1 x\ | 2*(2 + x) + 6*x 12*log(-1 - x)| | || log(-1 - x) 2 |
|||- + -|*|------------------- + --------------| for |2 + x| < 1| ||- ----------- + ---------- for And(x >= -3, x < -1)|
||\2 4/ | 4 3 4 | | || 3 2 |
|| \(2 + x) - (2 + x) (2 + x) / | || (2 + x) 3*(2 + x) |
|| | || |
|| oo | || oo |
|< ____ | + |< ____ |
|| \ ` | || \ ` |
|| \ n | || \ n |
|| \ n*(2 + x) | || \ (2 + x) |
|| / ---------- otherwise | || / -------- otherwise |
|| / 3 + n | || / 3 + n |
|| /___, | || /___, |
\\ n = 0 / || n = 0 |
\\ /
Piecewise(((1/2 + x/4)*((2*(2 + x)^2 + 6*x)/((2 + x)^4 - (2 + x)^3) + 12*log(-1 - x)/(2 + x)^4), |2 + x| < 1), (Sum(n*(2 + x)^n/(3 + n), (n, 0, oo)), True)) + Piecewise((-log(-1 - x)/(2 + x)^3 + (-6 - 3*x/2)/(3*(2 + x)^2), (x >= -3)∧(x < -1)), (Sum((2 + x)^n/(3 + n), (n, 0, oo)), True))
Ejemplos de hallazgo de la suma de la serie
- Suma de la serie de potencias
x^n/n
(x-1)^n
- Factorial
1/2^(n!)
n^2/n!
x^n/n!
k!/(n!*(n+k)!)
- Serie de Flint Hills
csc(n)^2/n^3
- Serie de cuadrados inversos
1/n^2
1/n^4
1/n^6
- Serie armónica
1/n
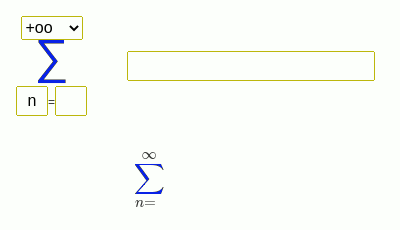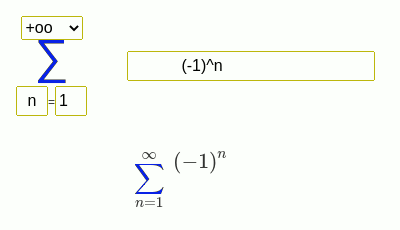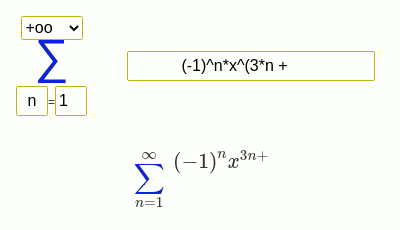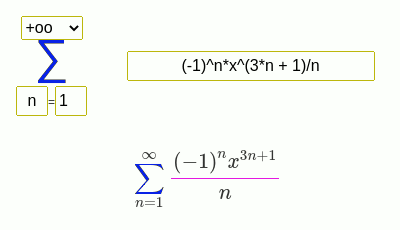
- Serie de Grandi
(-1)^n
- Serie alternada
(-1)^(n + 1)/n
(n + 2)*(-1)^(n - 1)
(3*n - 1)/(-5)^n
(-1)^(n - 1)*n/(6*n - 5)
- Serie de Newton-Mercator
(-1)^(n + 1)/n*x^n
- Investigar la convergencia de la serie
(3*n - 1)/(-5)^n

 (n/(2*n+1))^n
(n/(2*n+1))^n
 (5^n+2^n)/10^n
(5^n+2^n)/10^n
 (2/7)^n
(2/7)^n